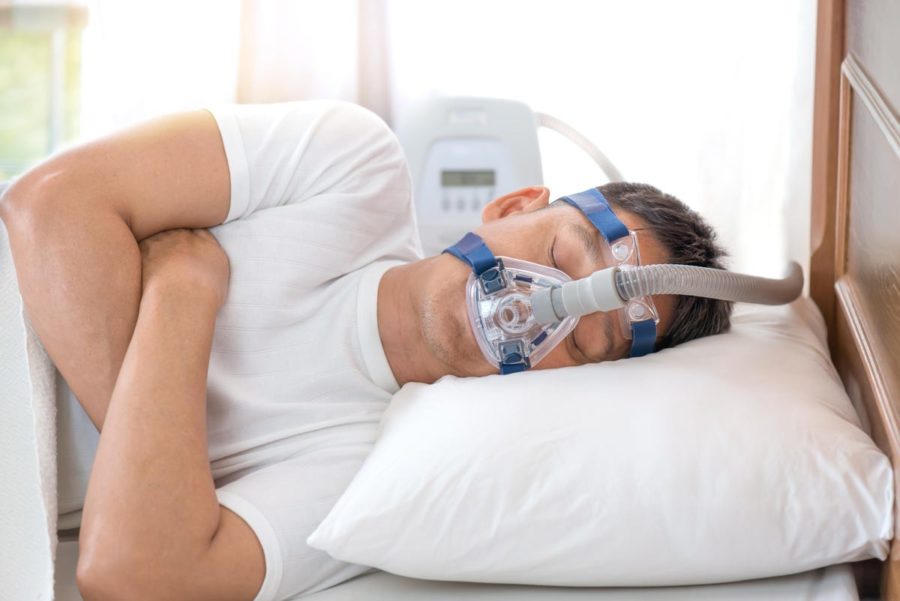
Sleep Apnea-
Being more physically active and spending fewer hours watching TV could substantially boost your health.
The following written content by Elizabeth Millard

Looking for the motivation to pivot away from your latest viewing binge and get out for a run? Well, consider this: Being physically active and spending fewer hours watching TV could substantially lower your risk of developing obstructive sleep apnea, also called OSA, according to new research in the European Respiratory Journal.
That’s a big deal, since OSA is considered a serious condition where breathing stops and starts while you’re sleeping. Not only does this disrupt your sleep and lead to daytime sleepiness, but it also reduces oxygen levels in the blood and boosts your risk of cardiovascular problems and type 2 diabetes.
To gauge the extent of the association, researchers looked at health data from more than 138,000 men and women in the U.S. who weren’t diagnosed with OSA at the study’s start. By the end of the research timeframe—about 10 to 18 years, depending on participant surveys—those who had a higher activity level were about 54 percent less likely to develop OSA.
Sitting and watching TV was especially problematic, and participants who reported more than four hours daily of that habit had a 78 percent higher risk of OSA than the least sedentary people. Even sedentary work, like an office job, had less risk involved, according to lead author Tianyi Huang, D.Sc., associate epidemiologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and assistant professor at Harvard Medical School in Boston.
That doesn’t mean you’re off the hook if you mainly sit in your job, though, he told Bicycling.
“Both types of sedentary behavior are associated with sleep apnea risk,” he said. “The difference is that watching TV is more strongly correlated with obesity measures. This could be due to other behaviors co-occurring with TV watching, like snacking or drinking sugar-sweetened beverages.”
Obesity is the strongest risk factor for sleep apnea, Huang added. Being active has been shown to improve insulin resistance and to lower inflammation, he said. These are vital mechanisms when it comes to sleep apnea, as well as body fluid retention. He said an activity like running during the day can reduce how much fluid you retain at night—which means less pressure on the lungs when you’re sleeping.
Another important takeaway is that for better sleep health, it’s not enough to just be less sedentary—getting exercise like running is also essential.
“People can have high levels of physical activity while also being very sedentary,” said Huang. “What our study suggests is that you have to do both. Not only should you get more active, but you also need to reduce sedentary hours.” Read more from Runner’s World.