This is the world’s oldest family tree created using DNA-
Scientists have compiled the world’s oldest family tree from human bones interred at a 5,700-year-old tomb in the Cotswolds, UK.
The following written content by Paul Rincon
Analysis of DNA from the tomb’s occupants revealed the people buried there were from five continuous generations of one extended family.
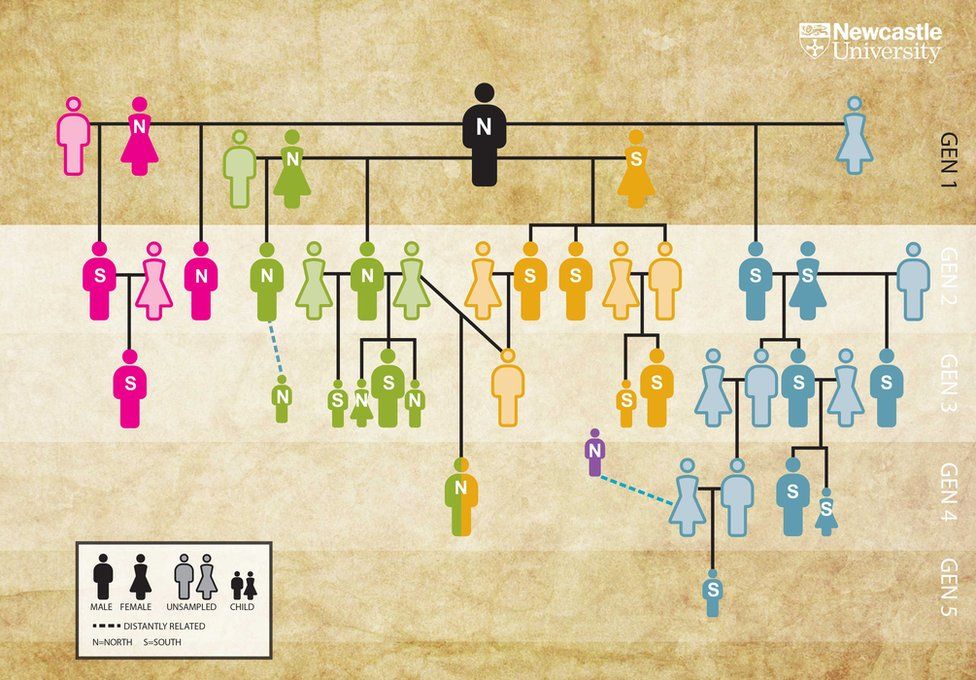
Most of those found in the tomb were descended from four women who all had children with the same man.
The right to use the site was based on descent from one man.
But people were buried in different parts of the tomb based on the first-generation matriarch they were descended from.
This suggests that the first-generation women held a socially significant place in the memories of this community. The Neolithic tomb, or “cairn”, at Hazleton North in Gloucestershire has two L-shaped chambers, one facing north and the other south.
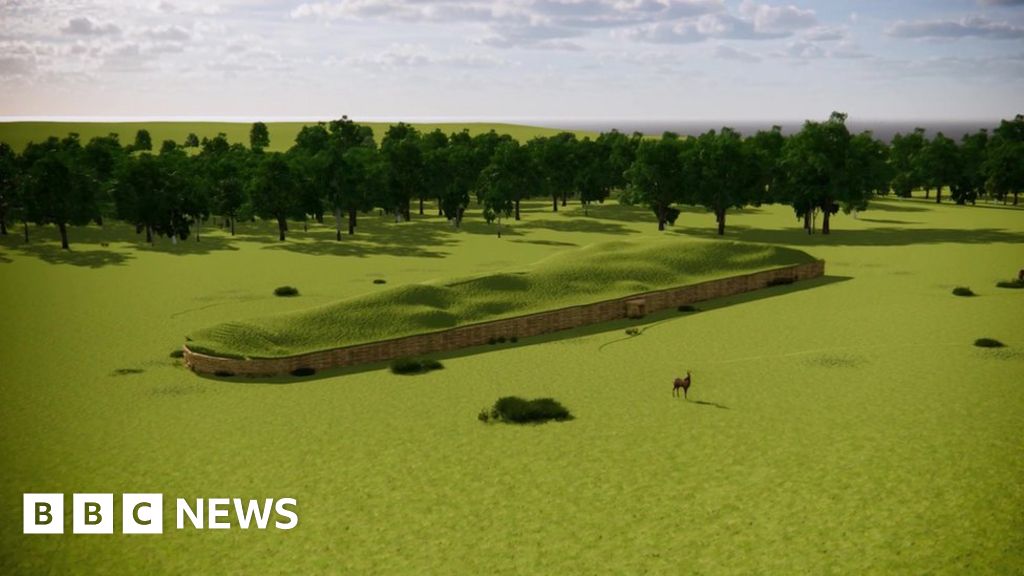

Co-author Prof David Reich, from Harvard Medical School in Boston, US, who led the generation of ancient DNA from the remains, explained: “Two of the women, all of their children are in the south chamber – and their kids up to the fifth generation.
“And then the other two women, their kids are primarily in the north chamber – although some of them switch to the south chamber later in the use life of the tomb – probably reflecting the collapse of the north passage which meant it wasn’t possible to bury there anymore.”
Dr Chris Fowler of Newcastle University, UK, the first author and lead archaeologist in the study, said: “This is of wider importance because it suggests that the architectural layout of other Neolithic tombs might tell us about how kinship operated at those tombs.”
The tomb dates to an important period just after farming was introduced to Britain by people whose ancestors had – several thousand years earlier – spread into Europe from Anatolia (modern Turkey) and the Aegean. The work will help researchers understand family dynamics among these Stone Age people and learn more about their culture.
“Hopefully this will be the first of many such studies,” said Prof Reich. “It really makes vivid the lives of these people… who lived in this place a very long time ago.”
There are also indications that “stepsons” were adopted into the family, the researchers say – males whose mother was buried in the tomb but not their biological father, and whose mother had also had children with a male related to the original founder. Read more from BBC.
Here’s another video for your interest:





